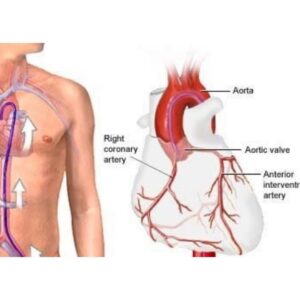
Angiography is a popular medical treatment that allows doctors to see how blood flows throughout the body. A multitude of medical conditions may necessitate diagnosis. It also allows for intervention and treatment of blockages and other problems, particularly those affecting the heart and brain.
Find out why it’s done, how it’s done, the risks and side effects, and how long it takes to recover from angiography